Essential Hemodynamic Monitoring Lessons from the ICU: A Comprehensive Guide

Hemodynamic monitoring is a critical skill for any healthcare professional working in intensive care units (ICUs). It allows clinicians to assess the cardiovascular status of critically ill patients and make informed decisions about their care. However, hemodynamic monitoring can be complex and challenging, especially for those who are new to the field.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of hemodynamic monitoring. We will cover the basics of cardiovascular physiology, the different types of hemodynamic monitoring devices, and how to interpret hemodynamic data. We will also discuss the use of hemodynamic monitoring to guide fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and inotropic support.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 42815 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 621 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 480 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.7 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.5 x 1 x 9.5 inches |
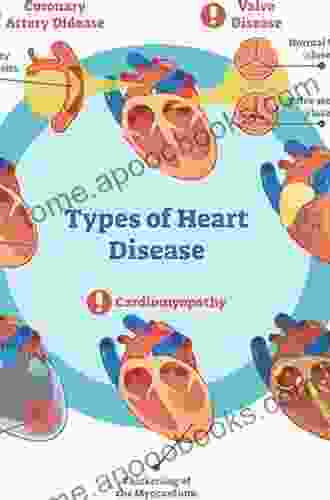
Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Physiology
In Free Download to understand hemodynamic monitoring, it is important to have a basic understanding of cardiovascular physiology. The cardiovascular system is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It consists of the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood.
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood through the body. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The blood vessels are a network of tubes that carry blood throughout the body. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood back to the heart. Capillaries are small blood vessels that connect arteries and veins.
Blood is a fluid that contains red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the tissues. White blood cells fight infection. Platelets help to stop bleeding. Plasma is the liquid part of blood.
Chapter 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring Devices
There are a variety of different hemodynamic monitoring devices available. The most common types of devices are:
- Arterial line catheters
- Central venous pressure (CVP) catheters
- Pulmonary artery catheters (PACs)
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
Each type of device has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of device will depend on the specific needs of the patient.
Chapter 3: Interpreting Hemodynamic Data
Hemodynamic data can be used to assess the cardiovascular status of a patient. The most important hemodynamic parameters are:
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Central venous pressure (CVP)
- Pulmonary artery pressure (PAP)
- Cardiac output
These parameters can be used to assess the patient's volume status, cardiac function, and vascular tone.
Chapter 4: Fluid Resuscitation
Fluid resuscitation is an important part of the management of critically ill patients. Fluids can be used to restore intravascular volume, improve cardiac output, and reduce tissue perfusion.
The choice of fluid will depend on the patient's underlying condition. Crystalloids are typically used for volume resuscitation, while colloids are used for patients who are at risk for hypoalbuminemia.
Chapter 5: Vasopressor Therapy
Vasopressors are medications that are used to increase blood pressure. They are typically used in patients who are in shock.
The choice of vasopressor will depend on the patient's underlying condition and hemodynamic status. Norepinephrine is the most common vasopressor used in the ICU.
Chapter 6: Inotropic Support
Inotropes are medications that are used to increase cardiac contractility. They are typically used in patients who have heart failure.
The choice of inotrope will depend on the patient's underlying condition and hemodynamic status. Dopamine is the most common inotrope used in the ICU.
Hemodynamic monitoring is a critical skill for any healthcare professional working in intensive care units. This comprehensive guide has provided an overview of the basics of cardiovascular physiology, the different types of hemodynamic monitoring devices, and how to interpret hemodynamic data. We have also discussed the use of hemodynamic monitoring to guide fluid resuscitation, vasopressor therapy, and inotropic support.
For more information on hemodynamic monitoring, please refer to the following resources:
- Society of Critical Care Medicine: https://www.sccm.org/
- American Heart Association: https://www.heart.org/
- National Institutes of Health: https://www.nih.gov/
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 42815 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 621 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 480 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.7 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.5 x 1 x 9.5 inches |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Sandy Alvarez
Sandy Alvarez Daniel Transon
Daniel Transon Astrid Avero
Astrid Avero Anthony Marra
Anthony Marra Anthony Wood
Anthony Wood Antoine Wilson
Antoine Wilson Richard Marman
Richard Marman H G Tudor
H G Tudor Audrey Niffenegger
Audrey Niffenegger Grateful Dead
Grateful Dead Anthony Bozza
Anthony Bozza Annie Rachel Cole
Annie Rachel Cole B K Froman
B K Froman Charles Fillmore
Charles Fillmore Todd F Lewis
Todd F Lewis Ayik Chut Deng
Ayik Chut Deng Ansh Vasani
Ansh Vasani Grizzly Publishing
Grizzly Publishing Nancy Marie Mithlo
Nancy Marie Mithlo Athena Floras
Athena Floras
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Colt SimmonsBind the Soul Steel Stone: A Literary Odyssey into the Depths of Magic and...
Colt SimmonsBind the Soul Steel Stone: A Literary Odyssey into the Depths of Magic and... Carlos DrummondFollow ·14.9k
Carlos DrummondFollow ·14.9k Dylan MitchellFollow ·4.1k
Dylan MitchellFollow ·4.1k Rick NelsonFollow ·18.1k
Rick NelsonFollow ·18.1k Ruben CoxFollow ·2.1k
Ruben CoxFollow ·2.1k Robin PowellFollow ·9.1k
Robin PowellFollow ·9.1k Hamilton BellFollow ·6.3k
Hamilton BellFollow ·6.3k Ivan CoxFollow ·13k
Ivan CoxFollow ·13k Thomas PynchonFollow ·5.1k
Thomas PynchonFollow ·5.1k

 Gabriel Garcia Marquez
Gabriel Garcia MarquezLad Dog Baby Professor: The Perfect Book for Your Child
Lad Dog Baby...

 Fredrick Cox
Fredrick CoxAn Excerpt With Fifty Ways To Help Animals Promo Books:...
: Embracing Animal...

 Kelly Blair
Kelly Blair5th Grade US History: Famous US Authors: Fifth Grade...
Step into a captivating world of historical...

 Natsume Sōseki
Natsume SōsekiKull the Destroyer: A Timeless Tale of Sword and Sorcery
The Creation of a...

 Jim Cox
Jim CoxDas Ist Supertoll: Unlocking the Magic of German for Kids
Immersive Learning with...

 Bruce Snyder
Bruce SnyderUnlock the World of Quilting for Kids: Discover "Quick...
Are you ready to embark on a delightful...
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 42815 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 621 pages |
| Hardcover | : | 480 pages |
| Item Weight | : | 1.7 pounds |
| Dimensions | : | 6.5 x 1 x 9.5 inches |